
Coupled with rising screen time across social media giants like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok, this data raises critical questions about our relationship with technology and its far-reaching implications on mental health.
Image: File.
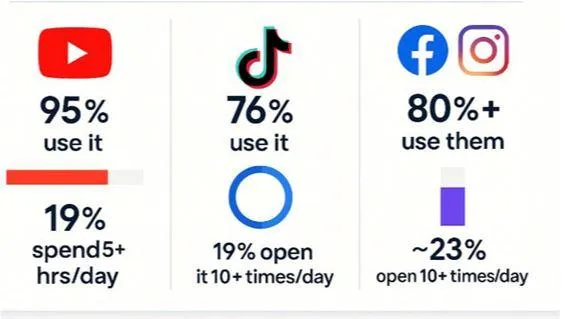
As we plunge deeper into the digital age, a new societal affliction is taking root: digital addiction. According to the recent Hooked in 2025 survey presented by Casinos Blockchain, a staggering 95% of U.S. adults engage with YouTube, affirming its status as the most habit-forming platform.
Coupled with rising screen time across social media giants like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok, this data raises critical questions about our relationship with technology and its far-reaching implications on mental health.
The survey, which sampled 1,000 participants, paints a vivid picture of how behavioural dependencies are evolving, with distinct patterns fluctuating across different age groups and platforms.
Addictive.
Image: Supplied
With nearly one in five users reporting over five hours spent daily on YouTube, and around 80% of respondents admitting to engaging frequently with social media, the scope of addiction is undeniable.
YouTube stands out prominently, with an unprecedented user engagement metric that reflects its critical role in habit-forming behaviours.
Over one-third of users check YouTube more than ten times daily, with extreme cases clocking upwards of five hours on the platform.
Following closely, Facebook and Instagram also demonstrate remarkably high levels of usage, particularly among younger demographics, indicating a concerning trend: social media is not just a pastime; it's an entrenched part of daily life.
TikTok, another major player in the social media space, captivates approximately three-quarters of respondents, showcasing how users cycle between multiple high-engagement platforms.
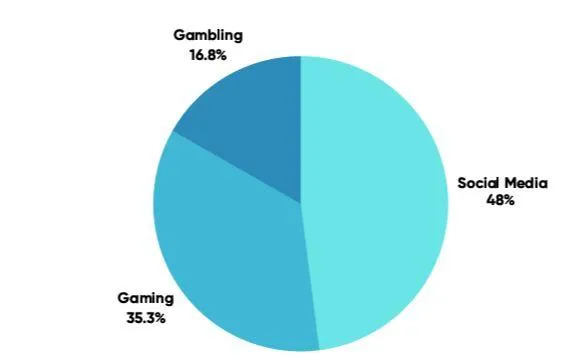
Coupled with rising engagement figures, it is evident that social networking apps dominate as the most addictive behaviour type, holding a firm grip over user attention and time.
The Hooked in 2025 survey exposed intriguing insights into user spending patterns as well.
While many keep expenditures limited, sizeable percentages report substantial monthly spending, particularly in subscription services and gambling.
Approximately 54% of respondents admitted to spending at least $30 monthly on subscriptions, reflecting the financial demand created by streaming platforms and premium content services.
In terms of addiction by age, the survey highlights a concerning trend: younger adults, particularly those aged 18-24, report the highest digital addiction levels.
Alarmingly, this demographic averages around 7-8 hours of social media use daily, with over 70% acknowledging feelings of addiction to digital activities.
Conversely, middle-aged respondents show higher involvement in gambling and alcohol, revealing a complex dynamic between digital and traditional vices.
G2
Image: Supplied.
One of the major revelations from the research entails the features that keep users engaged. Surveys identified “rewards and bonuses” — such as gamified systems and likes — as crucial engagement drivers, while push notifications and personalised content feeds also emerged as key hooks that compel users back to the platform. These elements collectively create a relentless cycle of engagement that undermines users' intent to limit screen time.
The societal costs of digital addiction are staggering. With estimations placing the cost of digital addiction at approximately $3 trillion annually in lost productivity and economic output, the scale of this issue reaches far beyond individual experiences.
Furthermore, the gambling industry alone generates over $110 billion, and global alcohol sales reach an alarming $1.7–2.1 trillion each year.
Yet, despite the clear health risks and financial implications, only about 19% of respondents have sought help for their digital compulsions, underscoring an urgent need for awareness and intervention strategies.
Particularly among Gen Z, there is an inclination to seek support, but opportunities remain limited, particularly for older demographics.
Looking ahead, the challenge lies not only in mitigating the risks of digital addiction but also in fostering a healthier relationship with technology.
The data collected in this survey illustrates an alarming reality: as platforms optimise for engagement through targeted psychological hooks, society must grapple with the consequences on well-being and productivity.
Without proactive prevention and intervention strategies, digital addiction is set to become an ever-more entrenched aspect of modern life.
BUSINESS REPORT
Visit: www.businessreport.co.za