The future of finance has arrived with the latest CIMA CGMA Professional Qualification upgrade
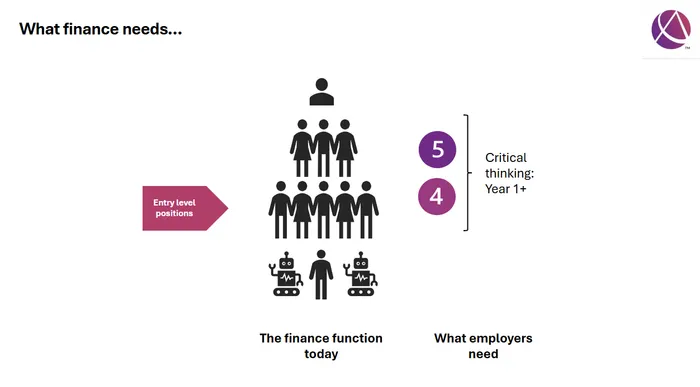
The upgraded CGMA Professional Qualification syllabus enables students to develop critical thinking skills from day 1, Image: Supplied
Image: Supplied
To succeed in a digitally enabled business world, finance professionals must not only possess sound technical accounting and finance skills but also be able to combine them with critical thinking, technology, and high-performance business partnering skills. This is the future of finance.
The good news? The Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA) CGMA Professional Qualification has been upgraded to help finance professionals do just that.
Even better, we’re introducing skills most in demand by employers earlier in your learning journey—without increasing the difficulty of the exams. CIMA’s commitment is to continuously evolve the syllabus, keeping you aligned with the latest professional standards and business practices.
And there’s no need to worry about disruptive changes. As it rolls out the 2026 syllabus or future upgrades, you won’t be required to take additional modules or meet tight deadlines to complete your qualification.
So why the upgrade?
Just five years ago, most finance teams operated within a traditional pyramid structure: a broad base of entry-level roles narrowing toward senior leadership positions like Finance Director or CFO. But in 2019, its landmark Future of Finance: Reinventing finance for a digital world report predicted a technology driven shift that would fundamentally reshape this model.
What CIMA didn’t fully anticipate was the speed of this transformation.
Fast forward to 2024. The world has changed—and so has the finance profession. CIMA’s follow-up global report, Future of Finance 2.0: Re-defining finance for a sustainable world, published last year confirmed that transformation is well underway. Many finance functions are already leveraging AI to automate routine tasks, freeing up time for professionals to focus on higher-value activities like problem solving, analysis, decision support, and strategic recommendations.
This evolution made the mission for the upgraded Chartered Global Management Accountant Professional Qualification (CGMA Professional Qualification) clear: to accelerate the development of high-performing finance business partners. That means embedding critical thinking skills earlier in the learning journey and expanding the syllabus to cover areas such as sustainability and generative AI (GenAI).
Developed by finance professionals for finance professionals, the CGMA Professional Qualification equips learners with the knowledge and capabilities to drive strategy, support decision-making, and deliver value across both private and public sectors. It opens doors to countless career opportunities for CGMA designation holders.
In this new era, finance is no longer just about reporting the numbers. It’s about shaping the future. Finance roles are being refined to meet the future demands of business and economies. Finance professionals need to be equipped with the right technical and critical thinking skills, a strong understanding of their organisation, and the ability to analyse, assess, influence and lead. They must be capable of providing the insights their organisations need to craft and successfully execute their strategies.
The CIMA Qualification Framework – accelerating capabilities for the future of finance
The CGMA Professional Qualification consists of three levels - Operational, Management, and Strategic levels – culminating in a Case Study business simulation exam. The syllabus is a blend of accounting, finance, and management content essential business leadership. It covers areas such as strategy, performance and financial management, resource allocation, corporate reporting, risk management and sustainability. The qualification prepares individuals for diverse roles and levels across various sectors, including careers in finance, marketing, IT, operations, sustainability and business management.
To keep pace with the rapid transformation of business, the 2026 upgrade to the CGMA Professional Qualification introduces a bold new professional educational approach to developing the skills modern finance professionals need.
CIMA’s moved beyond the traditional, linear model of learning. Instead, it’s adopted a spiral curriculum—a dynamic framework that builds and reinforces interrelated skills at every stage of the qualification. This means students don’t simply accumulate knowledge level by level—they revisit and deepen their ability to solve increasingly complex business problems and add value as they progress.
From day one, learners begin developing critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills—no longer waiting until the final stages of their qualification. The result? They’re equipped to tackle real-world business challenges early in their journey and deliver meaningful value to their employers from the outset
What does this mean in practice?
At the heart of the 2026 CGMA syllabus upgrade is a shift in focus—from simply acquiring knowledge to demonstrating real-world competencies. The syllabus is now structured around the roles and responsibilities found in today’s modern finance functions, ensuring that what students learn directly aligns with what employers need.
In a world where information is readily accessible, technical knowledge alone is no longer a differentiator. What sets finance professionals apart is their ability to apply that knowledge—accurately, effectively, and strategically. This is where true professional value is created. Today’s finance leaders must become T-shaped professionals—combining deep technical expertise with a broad set of complementary skills such as communication, collaboration, and critical thinking.
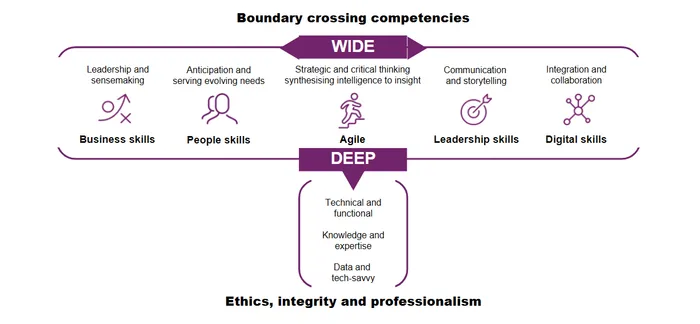
The T-shaped finance professional, Image: Supplied
Image: Supplied
One of the most powerful tools in this transformation is CIMA’s Case Study exams. These are not theoretical exercises—they’re grounded in real world job roles and responsibilities across all levels of an organisation. Students are challenged to solve real-world business problems, starting with well-defined scenarios at the Operational level and progressing to increasingly complex and ambiguous challenges at the Management and Strategic levels.
Through this problem-based learning approach, students develop essential skills like critical thinking, decision-making, and finance business partnering. They learn to solve problems through practical simulations, preparing them to deliver value from day one—and to grow into the strategic finance leaders of tomorrow
What will you learn and what is new?
For those unfamiliar with the it, the CGMA syllabus consists of three levels, compromising of nine subjects organised across three pillars.
These levels provide a scaffolded approach to qualification progression, building students’ knowledge and technical skills as they advance. Each level introduces increasingly complex problems and scenarios, helping students develop the power skills necessary for professional success.
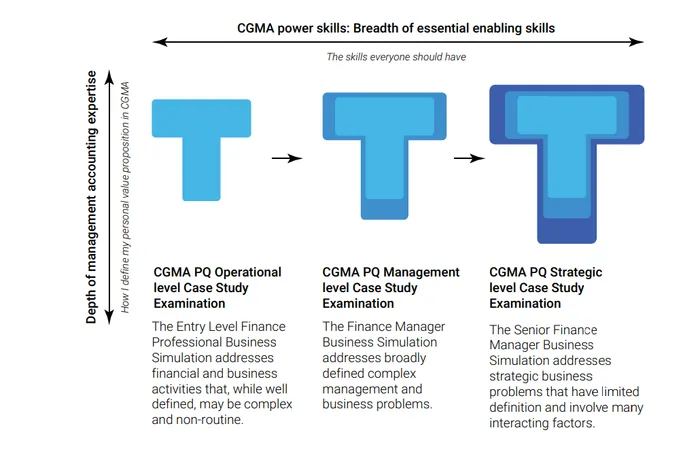
CIMA’s redrawn the CGMA Professional Qualification to reflect the changing roles of finance professionals, Image: Supplied
Image: Supplied
This structure aligns learning and Case Study business simulation exams at the Operational, Management, and Strategic levels to roles that reflect the shape and evolution of the modern finance function.
- The Operational level focuses on the short term and the implementation of decisions. Students learn to work collaboratively across the organisation and use relevant data and technology to translate medium-term decisions into actionable short-term plans.
- The Management level focuses on translating long-term decisions into medium-term plans. Students develop the ability to manage performance, allocate resources, monitor and report on decision implementation, and prepare and interpret financial statements to evaluate performance, using data and relevant technology throughout.
- Students develop the ability to manage performance, allocate resources, monitor and report on decision implementation, and prepare and interpret financial statements to evaluate performance, using data and relevant technology throughout
- The Strategic level focuses on long-term strategic decision-making that drives value creation. Students will be able to support organisational leaders to craft strategy, source financing to implement the strategy, perform valuations, and manage the risks that might prevent the successful implementation of strategy.
The three pillars represent specific areas of knowledge. The content of each pillar develops as students move up the qualification. The three pillars are interlinked to provide a coherent body of knowledge that will equip successful students with the competencies they require.
- The Enterprise pillar Focuses on the role of the finance function and its interaction with the wider organisation through the use of data and technology. It explores business models, as well as the management of people and projects to achieve organisational goals. The pillar also addresses the formulation and effective implementation of strategy.
- The Performance pillar applies the tools and techniques of management accounting and risk management assess the feasibility of strategy and monitor its execution. Students learn how to apply cost understanding to budgeting, pricing, capital expenditure decisions, cost control, and performance management. Digital costing is introduced alongside traditional costing techniques and cost management is expanded to reflect its growing importance in an increasingly competitive environment for organisations. Students also progressively develop the ability to identify, classify, and evaluate risk, including enterprise, strategic, and cyber risks and manage them primarily through internal controls.
- The Financial pillar focus is the financial accounting and reporting obligations of the organisation. This includes an understanding of the regulatory framework and external reporting requirements, including integrated reporting. The ability to construct and evaluate complex financial statements, including those relating to group accounts to show the financial position and performance of an organisation is essential. The pillar also includes principles of taxation, the tax implications of financing decisions, and the formulation of financial strategy linking to strategy development in the Enterprise Pillar and risk assessment in the Performance Pillar.
Each pillar’s subjects follow a structured learning path from Operational to Strategic level, ensuring a continuous and practical development of knowledge, tools, and capabilities aligned with the evolving demands of the finance profession.
What’s new for 2026?
Starting with the May 2026 Case Study exams, the CGMA Professional Qualification has been enhanced to reflect the evolving demands of the finance profession, with a stronger emphasis on sustainability and technology. —particularly in sustainability and technology.
Key updates include:
- Expanded sustainability content: All subjects now feature extended coverage of sustainability topics, such as environmental costing, green financing, and the latest IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards (S1 & S2).
- Enhanced technology focus: Building on existing tech content, the syllabus now incorporates GenAI and explores how AI-driven transformation is redefining working practices across finance functions.
- Evolved Case Study exams: The Case Study business simulation exams have been updated to reflect real-world challenges, including current and emerging issues particularly those related to sustainable business practices. These simulations are designed to assess students’ ability to apply their knowledge in dynamic, practical scenarios that mirror the complexities of modern finance roles.
To help students and educators navigate these changes, CIMA’s provided a summary table below outlining the key enhancements and clarifying what’s expected at each level of assessment.
Flexible routes to earning the CGMA designation
CIMA is not only leading the future of finance through its upgraded CGMA syllabus—it’s also reimagining how students can become CGMA designation holders. Today, there are four flexible routes, each designed to suit different learning styles, career stages, and levels of experience:
- Traditional exam route
This well-established path combines structured objective tests with Case Study exams, allowing students to progress at their own pace. It’s ideal for those who prefer a self-directed, exam-focused approach. - CGMA Finance Leadership Program
Launched in the UK in 2023, the CGMA Finance Leadership Program offers a digital-first, subscription-based learning experience. It features continuous assessment and Case Study exams, making it perfect for learners who thrive in a more flexible, interactive environment. - Experiential routes for experienced professionals
For seasoned finance professionals, CIMA offers tailored pathways through the Professional Gateway, Senior Executive, and CFO Programmes. These routes recognise prior experience and focus on completing Case Study exams to earn the CGMA designation. - Apprenticeship pathways
We also support Level 4 and Level 7 Apprenticeships, delivered in partnership with employers and training providers. These programmes allow students to earn while they learn, gaining practical experience on their journey to becoming Chartered Global Management Accountants.
CGMA is the future of finance
Since its founding in 1919, CIMA has been at the forefront of advancing management accounting. With its singular focus on finance and business, the CGMA Professional Qualification continues to prepare future-ready professionals to meet the challenges and opportunities of a rapidly evolving financial landscape.